- Dependencies and Installation
- Running AHA-GUI
- AHA-GUI Main Window Walkthrough
- New Run AHA-Scraper from AHA-GUI
- Remote databases
- AHA-GUI Data View Walkthrough
- Attack Surface Scoring methodology
Dependencies and Installation
AHA-GUI requires the current release of Java 1.8.0+. We suggest OpenJDK on *nix platforms or AdoptOpenJDK.net installers for macOS™ and Windows™. The Oracle Java installers will work as well, but their recent license changes have made it (in our opinion) more trouble than they are worth to install, thus we only test against OpenJDK on Linux distributions, and AdoptOpenJDK 1.8 and JDK11 LTS on macOS and Windows. While we attempt to test things as much as possible, we are researchers. We also only test current releases of JDKs (i.e. if current for 1.8 is 1.8.0_232, we don’t test prior to update 232). There is no warranty or guarantee this software will work as expected.
Get the current built and zipped version from our AHA-GUI Releases Page and unzip it in a place of your choosing.
Note: If you would like to build from source there are additional requirements and instructions, please refer to the readme in the AHA-GUI repository for more info.
About Java Runtimes
JDK8 or JDK11 are tested; JDK12 and later should work but are not tested against. Regardless which version you chose we recommend you always keep it updated. We will never advise you to stick with a particular version of Java within a major version, though we may advise you to steer clear of a particular version should we ever find an issue/regression/etc.
Windows/MacOS: For those who do not wish to create oracle accounts or deal with their licensing (though their JRE/JDK will run this fine), AdoptOpenJDK has precompiled OpenJDK installers for several platforms. Amazon with their Amazon Corretto progam which also provides a similar set of precompiled installers which they advertise as “No-cost, multiplatform, production-ready distribution of OpenJDK”
Linux: We would recommend whatever OpenJDK is in your package manger for the linux platform you’re on. OpenJDK8 will suffice, in brief testing, OpenJDK11 may see better graphics performance on Linux. Using the command line flag -Dsun.java2d.opengl=true (example java -Dsun.java2d.opengl=true -jar AHA-GUI.jar) may provide improved graphics performance.
Various tips/tricks/hints for platforms
MacOS: the Java8 JREs seem to provide a bit more performance (at least with graphstream), along with having HiDPI (Retina) support that works correctly with graphstream. Depending on various items, Java8 may not allow the menubar to move to the top of the screen macOS menubar location. JDK11 works well on non-retina machines that do not have performance issues.
Windows: No major recommendations for Java 8 vs Java 11.
Linux: Java 11 seems to have better performance by default.
Running AHA-GUI
- When you start the GUI it will ask you which file you would like to open. The other instructions about moving files or running with command line arguments to select file still work, but are no longer required.
Move or copy theBinaryAnalysis.csvoutput from AHA-Scraper into the directory that contains AHA-GUI.jar- To start AHA-GUI either double click
AHA-GUI.jaror open a terminal/powershell and cd to the correct directory and typejava -jar AHA-GUI.jar
If you invoke from the commandline, the following commandline arguments can be used:
- –debug : print additional information to console while running
- –verbose : print additional information to console while running, but not as much as debug. Useful for troubleshooting issues with input files.
- –single : use single lines between nodes with multiple connections
- –bigfont : use 18pt font instead of the default 12pt font (good for demos)
- –forceJMenu : on macs, force use of normal JMenu rather than using the traditional macOS menubar at the top of the screen
- –notheme : attempt to minimize theming information set on gui components so that the OS theme will be used. Unsupported / components may be oddly sized.
- –noforcescale : ignore the app attempting to force the scale down to 100% to avoid several existing graphstream bugs.
- –updateFile : update a given inputFile with information about attacksurface/threats from internet sources (presently aDolus)
- scorefile=scorefile.csv : use the scorefile specified after the equals sign
- inputFile=inputFile.csv : use the inputFile specified after the equals sign
- credsFile=inputFile.csv : use the credsFile for the credentials to update the input file (used with –updateFile) specified after the equals sign
As of v0.7.0 or later, these command line options can be set as defaults in the File -> Preferences. Be sure to click the save button. Settings are applied at next launch of AHA-GUI.
Example of AHA-GUI running:
AHA-GUI Main Window Walkthrough
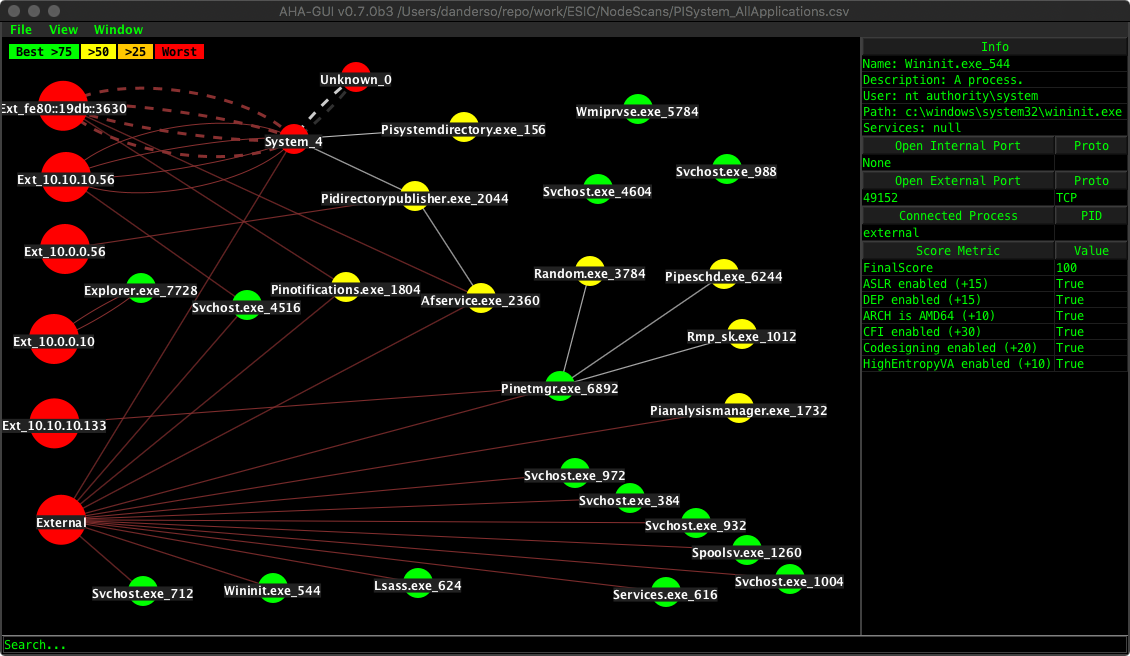
In the above image we can see AHA-GUI as it appears at launch. The lefthand side is the main AHA-GUI view area, the righthand side is the Graph Node Inspector which shows details of the graph nodes when they are clicked.
The main GUI is largely comprised of the graph view which shows external connections in red, internal connections in white, and duplicate connections in darker versions of each of those colors (i.e. darker red, and gray for duplicate connections). Connections in TIME_WAIT, CLOSE_WAIT, SYN_SENT, etc. are drawn as a dashed line. All solid connections with the exception of the connections drawn to the “External” virtual node are established connections.
The “External” virtual node is drawn to help visualize any service which has a port bound that would allow connection from an external entity. This node can be hidden by selecting “Hide Ext Node” from the bottom area of the main graph view.
An Example Video Demo of AHA-GUI Features (link to video hosted on youtube) is also available:
Along the bottom of the main AHA-GUI window there is a search bar. The search bar allows graph nodes/edges to either be emphasized (highlighted/edged in blue) or hidden (entirely hidden from the graph). Example syntax for the search bar:
processname==svchost.exe will emphasize svchost.exe
~processname==spoolsv.exe will hide spoolsv.exe
processname!=svchost.exe will emphasize everything that is not svchost.exe
~processname==spoolsv.exe will hide everything that is not spoolsv.exe
These terms can also be OR-ed together with the || symbol:
processname==svchost.exe || ~processname==spoolsv.exe will emphasize svchost.exe and hide spoolsv.exe at the same time. Please note this syntax is lazily evaluated from beginning to end per token. This means we split the complex query up by || and then process starting with the leftmost term, moving rightward. Thus if there is any conflict between the terms, the rightmost will win.
Graph view options and other features can be accessed through the menus (as of 0.6.8 and later, previously they were buttons on the main application window). On macOS by default they will show up in the regular operating system menu bar on the top of the screen. All other platforms will have the menu at the top of each application window (or optionally on macOS if using the appropriate command line option).
File Menu:
- Open… : This allows you to select a file. If a file is currently loaded, this will be closed and a new file loaded.
- Open Data View : This opens the data view window which has a textual spreadsheet like representation of the graph data. This view will be explained in a later section of this document.
- Run AHA-Scraper… : On supported platforms (currently Windows only) this will run AHA-Scraper and pop up a progress window. Upon completion of the scan, the results will be loaded into AHA-GUI automatically. The default scan length target of 15s is used and is currently not configurable. For more options, run AHA-Scraper manually.
- Update File… : This will attempt to use remote database credentials (default stored in credentials.txt in the same directory as AHA-GUI.jar) to update the currently opened file with information from the remote database, and then reload the resultant updated file.
- Preferences: This will open AHA-GUI’s preferences panel which allows you to set your preferences to be used each time you launch AHA-GUI.
- Exit : Exits AHA-GUI.
View Menu:
- Hide Windows Operating System Processes : Hides operating system processes which can sometimes clutter the view such as svchost.exe, spoolsv.exe, lsass.exe, and others. This is presently defined by an internal list of application paths, which will probably some day be split out into a config file similar to MetricsTable.cfg
- Show External Node : this will show/hide the virtual “External” node and all connections to it to help unclutter the graph.
- Use DNS Names : switches Ext_
format names to Ext_ . Example: would switch "Ext_10.0.0.1 to Ext_SomeHost". - Use Custom Scorefile : Overlays custom information from a custom scorefile. Default filename is scorefile.csv. There is an example for the custom scorefile in the AHA-GUI repository in the resources directory. You can use custom scorefile filenames by specifying scorefile=<path/to/customscorefile.csv> on the commandline when staring AHA-GUI.
—- - Show Only Matched Metrics : only show matched metrics (checked by default) which will only show the score rules which matched on the selected node.
- Show Score Metric Specifics : show metric specifics, which will show exactly which criteria matched.
- Update on MouseOver : updates the bottom summary view and graph inspector every time you hover over a new node on the graph rather than requiring a click on a node to update the info views.
— - Show Connectionless Nodes : Show nodes with no pipe/tcp/udp/etc connections to other nodes in the graph.
- Show Pipe : Show nodes which have named pipe connections between them.
- Show TCP : Show nodes which have TCP connections between them.
- Show UDP : Show nodes which have bound UDP sockets on the graph.
— - Normal Score Method : Normal uses the “Normal” score method described later which uses metrics from the MetricsTable.config located in the same directory as the AHA-GUI.jar.
- WorstCommonProc Score Method (Beta) : WorstCommonProc gives all processes with the same username the worst score for any proc under that user.
- Relative Score Method (Beta) : A beta score method that tries to use relative weights, and relativity to nodes that score poorly to weight neighbors
Window Menu:
- Reset Zoom: this button will reset the graph scale if things go awry, as they sometimes do.
New Run AHA-Scraper from AHA-GUI
As of v0.7.0 and later, AHA-GUI can run AHA-Scraper for you on supported platforms (currently Windows only). Using this feature from the File menu will run AHA-Scraper and pop up a progress window. Upon completion of the scan, the results will be loaded into AHA-GUI automatically. The default scan length target of 15s is used and is currently not configurable. For more options, run AHA-Scraper manually. You can read more about how to use it on the AHA-Scraper Basics documentation.
Remote databases
AHA-GUI supports looking up file hashes in remote databases. Currently aDolus, an ICS Whitelist database, is the supported option. Using the API Access page on aDolus, get your API key. Paste the key in a file called credentials.txt and put it in the same directory as AHA-GUI.jar. When loading a file with hashes (requires AHA-Scraper Windows v0.8.5+), you will be able to either use the –updateFile command line switch or use the Update File... command from the file menu. This will ask aDolus about each of the unique hashes found in the input file over an HTTPS connection, update the file with the results, and then reload the GUI (assuming the gui is running – not applicable if you’re just updating files using the cli method). Currently the aDolus file score, the quantity and numeric score of each CVE, the worst CVE (highest number), method of data entry into aDolus (partner submission, etc), and last time file was updated are what are written into the file after updating, and what are exposed in the GUI.
AHA-GUI Data View Walkthrough
There are presently two tabs in the Data View: Vulnerabilty Metrics, and Listening Processes.
Vulnerability Metrics
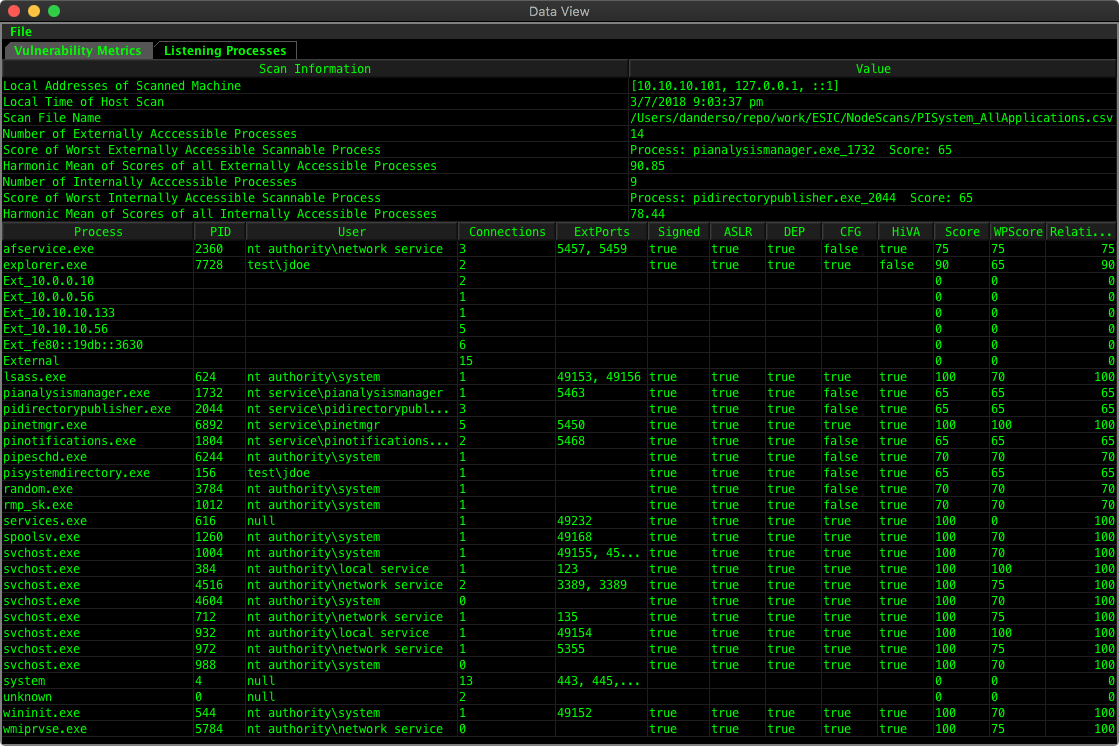
This view shows a summary of the evaluated graph, and also reflects what is produced in the AHA-GUI-Report.csv
The top portion shows overall statistics as well as when the scan data was taken/etc.
Below that is a table reflecting what is visible in the graph. Each row is a visible process/graph node, with useful data shown about each process, which is a much quicker way to compare things than attempting to click on each node in the graph and see values. Future versions will allow node highlighting in the graph based on clicks in the data view, and will probably allow multiple inspectors to also help facilitate process comparisons.
Listening Processes
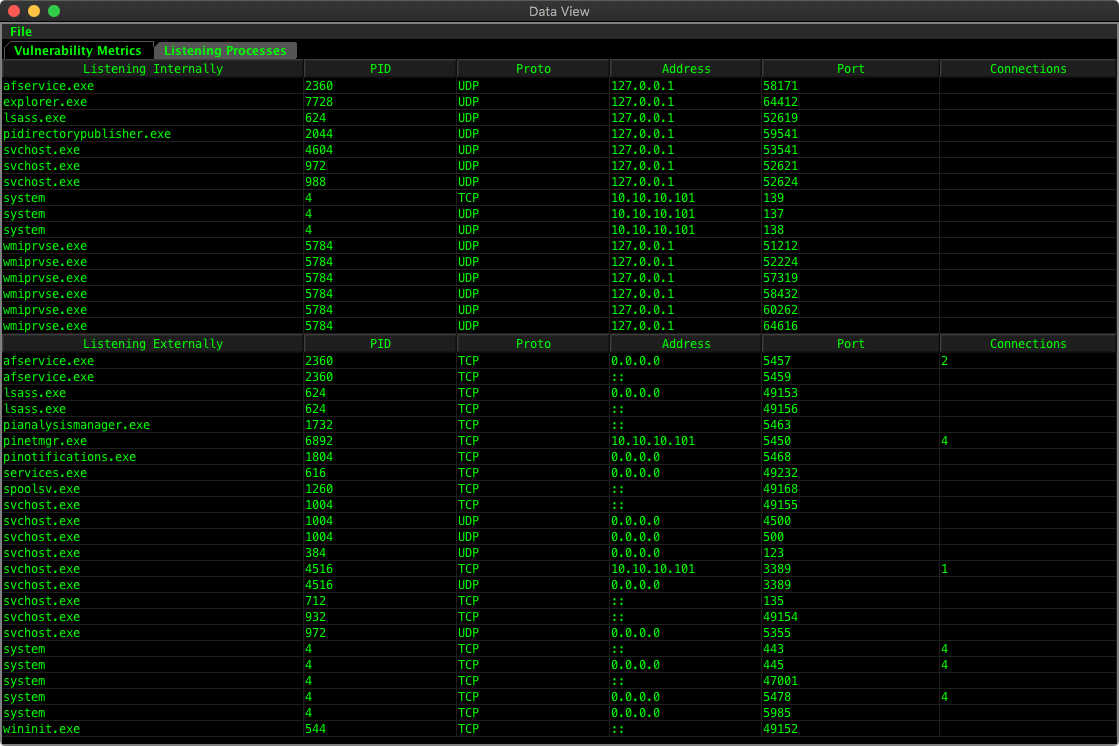
This view shows all bound ports visible in the graph, and which processes they are bound to, which helps give an overall view of services in the graph, as well as which are bound to internal only ports vs externally visible ports.
Attack Surface Scoring methodology
As noted above in the AHA-GUI walkthrough, there are several scoring methods, but we will start with the most basic. The standard scoring method used in AHA-GUI is called “Normal”. This applies rules from the MetricsTable.cfg located within the same directory as AHA-GUI.jar which is editable as a text file, and contains a default ruleset as well as an explanation of ho w to create new rules.
One thing to keep in mind for the scoring methods discussed in this section, is that they apply to the data that is available. In this case the data was gathered via CurrPorts, which is like a very advanced version of netstat (linux uses netstat and supporting other scripts), which provides us with processes and their open ports. We then make further passes on this data to determine security features of the executable binaries which are running for each process, as well as another pass to determine effective process privileges. While this is a very interesting dataset to analize please note that it does not as yet include any other platform specific security features such as ACL discovery, or reading of local machine firewall rules. This means that if the local firewall is active, that would impact established connections (i.e. they would probably not be established if that’s what the firewall is there to do), but we will still show ports that are bound on externally available IP address/Port combos as externally available. It is up to the user to audit their firewall/ACLs and ensure that the processes we discovered which could be available from external machines/networks/hosts/etc are properly firewalled.
In general, other scoring methods utilize the outputs of the “Normal” scoring algorithm, and are either assigning weight by positions in the node graph, or attempting to suss out other connections that are not visible via the tcp connection graph, such as connections by user account (WorstProcScore) or increase/reduction of attackability relative to the externally accessible nodes in the graph (ECScore).